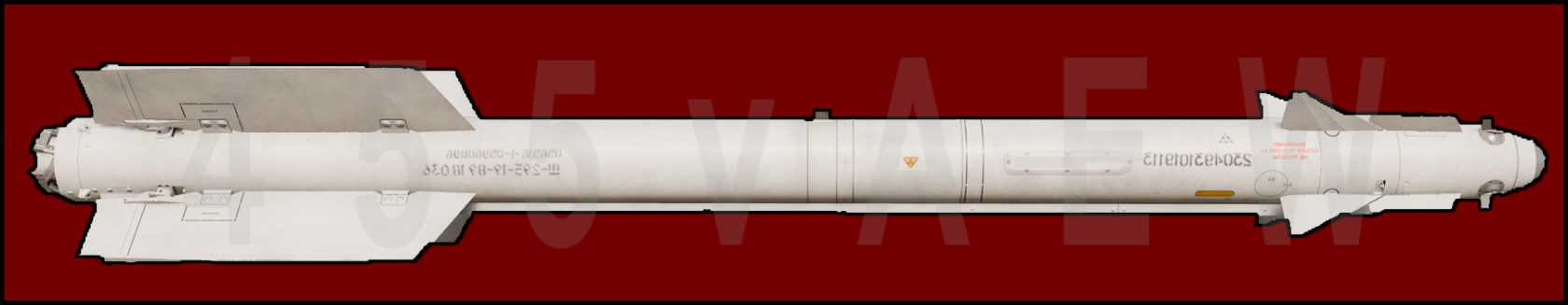
AA-11 "Archer"
| Date of Production | 1984 |
| Country of Origin | Russia (Former Soviet Union) |
| Proliferation: Algeria, Angola, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Belarus, Bulgaria, China, Cuba, Ethiopia, Hungary, India, Iran (Islamic Republic of), Malaysia, Myanmar, North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea), Peru, Poland, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Sudan, Uganda, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | |
Background
The Vympel R-73 (NATO reporting name AA-11 Archer) is a short-variety air-to-air missile that evolved with the aid of using Vympel NPO that entered service in 1984. The R-73 was evolved to update the sooner R-60 (AA-8 'Aphid') weapon for short-range use with the aid of using Soviet fighter aircraft. Work commenced in 1973, and the primary missiles entered service in 1984. The R-73 is an infrared homing (heat-seeking) missile with a sensitive, cryogenic cooled seeker with a substantial "off-boresight" capability: the seeker can "see" objectives as much as 40° off the missile's centerline. It may be centered with the aid of using a helmet-mounted sight (HMS) permitting pilots to designate objectives with the aid of using searching at them. The minimum engagement range is ready 300 meters, with the most aerodynamic variety of almost 30 km (19 mi) at altitude. The weapon is utilized by the MiG-29, MiG-31, Su-27/33, Su-34, and Su-35, and may be carried with the aid of using more recent variations of the MiG-21, MiG-23, Sukhoi Su-24, and Su-25 aircraft. India is seeking to use the missile on their HAL Tejas. It also can be carried with the aid of using Russian assault helicopters, along with the Mil Mi-24, Mil Mi-28, and Kamov Ka-50/52. In 1994, the R-73 has been upgraded in production to the R-73M standard, which entered CIS carrier in 1997. The R-73M has more variety and a much wider seeker angle (to 60° off-boresight), in addition to advanced IRCCM (Infrared Counter-Counter-Measures). Further tendencies encompass the R-74 (izdeliye 740) and its export variant RVV-MD. Russia presently gets new advanced air-to-air missiles on the idea of the R-73. An advanced model of the R-74, the K-74M (izdeliye 750) features fully digital and re-programmable systems, and is meant to be used at the MiG-35, MiG-29K/M/M2, Su-27SM, Su-30MK, and Su-35S. A similar upgrade, referred to as the K-74M2 (izdeliye 760), is meant for the fifth-generation Sukhoi Su-57 aircraft. This missile has decreased the move phase to healthy in inner weapon bays and could suit the overall performance of the AIM-9X and the ASRAAM. An easy sheet design, the K-MD (izdeliye 300), will supersede the K-74M2 in the future
Variants
General Characteristics
| Name | R-73; AA-11 Archer |
| Type | Infrared Homing Air-to-Air Missile |
| Manufacturer | Vympel NPO (current), Tbilisi Aircraft Manufacturing (current) |
| Length | 2.93 m |
|
Diameter
|
165 mm |
| Wingspan | 510 mm |
| Weight | 105 kg |
| Warhead Weight | 7.4 kg |
| Engine | solid-fuel rocket engine |
| Operational Range | R-73E: 30 kilometers (19 mi) R-73M1: 30 kilometers (19 mi) R-74: 40 kilometers (25 mi) |
| Maximum Speed | Mach 2.5 |
| Guidance System | All-aspect infrared homing |
| Launch Platform(s) | MiG-21, MiG-23-98, MiG-25, MiG-27, MiG-29, MiG-31, MiG-35 Sukhoi Su-24, Su-25, Su-27, Su-30, Su-33, Su-34, Su-35, Sukhoi Su-57 (future) Mil Mi-24, Mil Mi-28, Kamov Ka-50, Kamov Ka-52 Yak-141, Yak-130 HAL Tejas IRIAF F-14 J-10 |
Threat Characteristics
| Rear Aspect Range | 3 Nautical Miles |
| Front Aspect Range | 5 Nautical Miles |
| Countermeasure Vulnerability | Very Low |
Threat Counter Tactics Discussion
The AA-11
Threat Reactions
A