AA-12 "Adder"
| Date of Production | 1993 |
| Country of Origin | Russia |
| Proliferation: Algeria, China, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Peru, Russian Federation, Serbia, Sudan, Syria, Uganda, Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of), Viet Nam, Yemen | |
Background
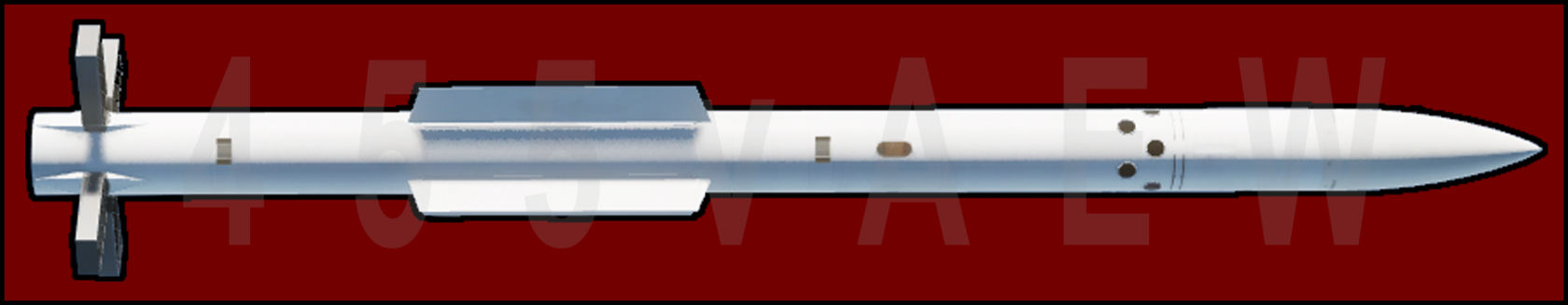
The maximum current Russian R-77 medium-variety missiles (AA-12 "AMRAAMSKI") is just like and in a few respects identical to the American AIM-120 AMRAAM missiles. The R-77 missile has an energetic radar finder and a most variety of 90-100 kilometers (50 km more than AMRAAM) and flies at 4 times the velocity of sound. The AA-12 has square slender span wings and a one of a kind set of 4 rectangular control surfaces on the rear. just like the configuration used at the terminal control fins of the SS-21 'Scarab' and SS-23 'Spider' ballistic missiles. These specific control surfaces function decreased flow separation at excessive angles of attack, producing extra aerodynamic moment force than traditional manage surfaces. The missile's steerage is inertial with mid-direction updates from the release plane, accompanied through a terminal energetic radar section from an acquisition range of approximately 20 kilometers. The Rocket was created particularly to offer the opportunity to apply practically from any aircraft equipped with way of measuring the goal coordinates (radar or optical), and the semi-energetic steerage enabled, if there are suitable skills of the radar, to set up numerous missiles on numerous targets. The R-77 missiles (the export name RVV-AE) belong to the fourth-technology air-to-air missiles. The missile is designed to destroy at all angles day and night, in one of a kind climate conditions, in opposition to the history of land and sea, below the impact of energetic radar jamming the subsequent objectives: notably maneuverable aircraft with an overload of up to 12 units, strategic bombers, helicopters and which include hover mode, missiles for numerous purposes (ground-to-air and air-to-air). Dimensions and mass of the missile, its design (small-extension wings and folding grilles) offer: the opportunity of the use of mild provider plane; massive ammunition carriage on medium and massive plane carriers; and the opportunity of conformal or internal placement. The R-77 is used withinside the armament device of MiG-29 and Su-27 warring parties of all modifications. The R-77 missile (RVV-AE) is made in the normal aerodynamic scheme (the rudders are placed at the back of the wings), with the X-fashioned and symmetrical arrangement of the wings and rudders. It includes 8 cubicles linked with the aid of wedge clamp packages. It makes use of non-detachable wings of ultra-small elongation and folded grating wheels, which may be in positions - folded (in the course of transportation and storage) or uncovered (whilst suspended below a provider plane). Each steerage wheel operates autonomously (kinematically now no longer linked with different steerage wheels) from a separate force motor. The R-seventy seven has a single-mode rocket engine with strong fuel. The aerodynamics are novel, combining vestigial cruciform wings with grid fins used as tail control surfaces (similar devices are used on the OTR-23 Oka, and USAF makes use of them on MOAB). Each floor includes a metallic body containing a blade-like grid meeting which mixes a extra manage area, and for that reason lifting pressure, with decreased weight and size. The improvement for this manage idea took 3 years of theoretical paintings and testing. These surfaces require much less effective actuators than traditional fins.[citation needed] The waft separation which happens at excessive angles of assault complements its turning ability, giving the missile a maximum turn rate of as much as 150° in line with second. However, up to date editions of the R-77, including the izdeliye a hundred and eighty this is destined for the Sukhoi Su-57, will use traditional fins instead. The missile makes use of a multi-characteristic doppler-monopulse energetic radar seeker evolved through OAO Agat. The radar capabilities modes of operation, over quick distances, the missile will release in an energetic "fire-and-forget" mode. Over longer distances the missile is managed through an inertial steerage car pilot with occasional encoded statistics hyperlink updates from the release plane's radar on modifications in spatial function or G of the goal. As the missile comes inside 20 km (12 mi) of its goal, the missile switches to its energetic radar mode. The host radar device keeps computed goal data in case the goal breaks the missile's lock-on.
Variants
General Characteristics
| Name | R-77 (AA-12 Adder) |
| Type | Long-range, active radar homing air-to-air missile |
| Manufacturer | |
| Length | 3.6 m (R-77), 3.71 m (R-77-1) |
|
Diameter
|
200 mm |
| Wingspan | 700 mm |
| Weight | |
| Warhead Weight | 22.5 kg HE fragmenting (R-77) |
| Engine | Solid fuel rocket motor (R-77), air-breathing ramjet (R-77-PD) |
| Operational Range | 80–100 km (R-77), 110 km (R-77-1) 193 km (R-77M) |
| Maximum Speed | Mach 4,Mach 5 for K-77PD (RVV-AE-PD) |
| Guidance System | Inertial with mid-course update and terminal active radar homing/infrared homing (R-77T) |
| Launch Platform(s) | MiG-21-93/LanceR/Bison, Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23, Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25, Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-27, Mikoyan MiG-29, Mikoyan MiG-31, Mikoyan MiG-35, Sukhoi Su-27, Sukhoi Su-30, Sukhoi Su-33, Sukhoi Su-34, Sukhoi Su-35, HAL Tejas, Yakovlev Yak-141, Chengdu J-10 |
Threat Characteristics
| Rear Aspect Range | 15 Nautical Miles |
| Front Aspect Range | 30 Nautical Miles |
| Countermeasure Vulnerability | Very Low |
Threat Counter Tactics Discussion
The AA-12
Threat Reactions
A

No Comments